Mongolia
Discover Mongolia
Mongolia, a landlocked country in East Asia, is known for its vast steppe, rugged mountains, and nomadic culture. With a rich history and unique traditions, Mongolia offers a fascinating blend of ancient and modern influences.

The country’s traditional nomadic lifestyle, beautiful landscapes, and vibrant cultural heritage make it an intriguing destination for travelers seeking immersive experiences. From the iconic Gobi Desert to the majestic Altai Mountains, Mongolia beckons adventurers and nature enthusiasts alike.
Mongolian National Flag and Symbols
The national flag of Mongolia features three vertical stripes of red, blue, and red, with the national emblem centered on the left-hand stripe. The red represents progress and prosperity, while the blue symbolizes the eternal blue sky. The national emblem consists of a combination of Buddhist symbols
and elements of traditional Mongolian design, reflecting the country’s rich cultural heritage and its strong ties to Buddhism. The Soyombo symbol, a unique and important national symbol, is also prominently featured on the emblem, representing freedom, strength, and unity for the people of Mongolia.

Additionally, the traditional symbols and motifs used in Mongolian art and crafts are deeply rooted in the country’s history and nomadic culture. These symbols often depict elements of nature, animals, and celestial objects, reflecting the spiritual connection to the environment and the importance of traditional beliefs and practices in Mongolian society.
Geography and Map of Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east, and west. Its vast, rugged terrain encompasses grassy plains, desert, and the Altai Mountains, as well as nomadic yurt camps and livestock. The Gobi Desert, known for its dinosaur fossils, also stretches across the south which adds an entirely different dimension to the country. The remarkable geographic diversity of Mongolia makes it a unique and fascinating destination for travelers seeking adventure and natural beauty.

Mongolia’s map reflects its expansive landscape, showcasing the various geographical features and attractions that make it a captivating travel destination. The map highlights the Gobi Desert, the Altai Mountains, the vast grasslands, and the numerous lakes and rivers that define the country’s geography.
The beauty of Mongolia’s geography and the richness of its natural wonders make it a must-visit location for nature enthusiasts and adventure seekers.
This image search query brings up visual representations of Mongolia’s diverse landscape and detailed maps that capture the country’s geographical features in an artistic and informative manner.
Currency and Economy of Mongolia
Mongolian Tugrik (MNT)
The official currency of Mongolia is the Tugrik (MNT). The Tugrik is recognized by the symbol “₮” and is issued by the Bank of Mongolia. It is subdivided into 100 möngö (мөнгө), and the currency is available in both coins and banknotes. The Tugrik has been the official currency of Mongolia since 1925 and plays a vital role in the country’s economic transactions and trade.

Economic Sectors
Mongolia’s economy is primarily driven by its rich natural resources, including coal, copper, gold, and other minerals. The agriculture sector also contributes significantly to the economy, with livestock farming being a traditional and vital economic activity. Additionally, tourism and the service sector have been growing in importance, especially in recent years.
Economic Challenges and Opportunities
While Mongolia’s economy has seen growth and development, it also faces challenges such as managing its resource wealth, sustainable development, and reducing dependency on mineral exports. The government has been proactive in seeking to diversify the economy and open up new sectors for investment, aiming for a balanced and sustainable economic growth path.
Traditional Culture and Customs in Mongolia
Distinctive Clothing
The traditional clothing of Mongolia reflects its nomadic lifestyle and harsh climate. The deel, a long, sturdy, and warm robe-like garment, is commonly worn by both men and women. It is often adorned with colorful patterns and designs, representing the wearer’s personal style and heritage.

Celebration of Naadam
Naadam is a traditional festival in Mongolia, celebrated with great pomp and grandeur. It includes competitions in the “Three Manly Games” – horse racing, wrestling, and archery. The festival showcases the Mongolian values of strength, agility, and prowess, and is deeply intertwined with the country’s nomadic culture.
Mesmerizing Throat Singing
One of the unique musical traditions of Mongolia is “throat singing” or “khöömei”. It is a mesmerizing form of singing where a single vocalist produces two distinct pitches simultaneously. This ancient singing
style is often accompanied by traditional instruments and plays a significant role in Mongolian cultural performances.
Traditional Mongolian Dance and Music
Traditional Mongolian Dance
Mongolian dance is an integral part of the country’s cultural heritage, with a history deeply rooted in nomadic traditions and shamanistic rituals. The dance forms, often accompanied by traditional music, reflect the daily lives, struggles, and celebrations of the Mongolian people. One of the most famous traditional dances is the “Bielgee,” characterized by graceful movements and vibrant costumes that symbolize the beauty of the Mongolian landscapes.

Traditional Mongolian Music
Mongolian music is known for its melodious tunes and unique throat singing, also known as “khöömei.” Throat singing is a mesmerizing vocal technique where singers produce multiple pitches simultaneously, creating an ethereal and harmonious sound that is deeply rooted in nomadic traditions. The Morin khuur, a traditional horsehead fiddle, is another iconic instrument that embodies the soulful melodies of Mongolian music.
Mongolian Traditional Food and Cuisine
Buuz (Mongolian Dumplings)
Buuz are a traditional Mongolian dish consisting of steamed filled pockets of dough. They are typically filled with minced meat, such as mutton or beef, and various seasonings. Buuz are commonly enjoyed during special occasions and festivals, and they hold cultural significance in Mongolian cuisine.

Tsagaan Idee (Milk Tea)
Tsagaan Idee is a creamy and salty milk tea that is a staple in Mongolian households. It is made from black tea, milk, and salt, sometimes with the addition of butter or rice. It is often served with traditional pastries such as boortsog (fried dough) or aaruul (dried curd).

Khuushuur (Fried Meat Pie)
Khuushuur is a popular Mongolian snack made of thin, unleavened dough filled with minced or ground meat, typically mutton, and deep-fried to a crispy golden brown. It is often enjoyed as street food and is a favorite during Naadam, the annual traditional festival.

Aaruul (Dried Curd)
Aaruul is a type of dried curd made from yogurt, cheese, or milk. It is a commonly consumed snack in Mongolia and is known for its long shelf life. Aaruul comes in various flavors and textures and is often eaten on its own or used as an ingredient in other dishes.

Mongolian Traditional Clothing and Attire
Deel
The Deel is the traditional and national costume of Mongolia. It is a long, loose-fitting robe with a high collar and is fastened with a sash. The Deel is designed to provide warmth and protection in the harsh Mongolian climate.
Deluun
The Deluun is a traditional Mongolian hat worn with the Deel. It is made of fur or brightly colored fabric and is an essential part of traditional Mongolian attire, often adorned with intricate patterns and designs.
Khantaaz
The Khantaaz, or Mongolian boots, are an integral part of traditional Mongolian clothing. They are made of sturdy leather and are designed to protect the feet in rugged and varied terrains.
Jewelry
Mongolian traditional attire is often adorned with intricate jewelry, including necklaces, bracelets, and rings, which hold cultural significance and craftsmanship.
Mongolian Traditional Festivals and Celebrations
Naadam Festival
Naadam is the most widely celebrated festival in Mongolia, often referred to as the “Three Manly Games” due to its focus on the traditional sports of wrestling, horse racing, and archery. The festival is deeply rooted in Mongolian culture and history, with origins dating back to the era of Genghis Khan. It typically takes place over three days in July and includes colorful opening ceremonies and cultural performances in addition to the sporting events.

Tsagaan Sar (Lunar New Year)
Tsagaan Sar, meaning “White Moon” in Mongolian, is the traditional New Year’s festival celebrated with great joy and enthusiasm. Families come together to participate in the rituals and customs associated with the holiday, including preparing and sharing special dishes, exchanging gifts, and visiting relatives. It is a time for expressing gratitude and renewing family ties, and it is considered the most important holiday in the Mongolian calendar.
Shoton Festival
The Shoton Festival, also known as the Yoghurt Festival, is a significant religious observance that marks the end of the fasting period for Tibetan Buddhists in Mongolia. It features the unveiling of a giant thangka (religious painting) and the distribution of yoghurt, symbolizing the end of the strict vegetarian diet followed by monks during the summer months. The festival includes colorful performances, traditional music, and dancing to celebrate the occasion.
Mongolian Traditional Sports and Games
Wrestling
Mongolian traditional wrestling, known as “Bökh,” is a centuries-old sport that holds a special place in the country’s culture. It is a full-contact wrestling style with strict rules and rituals. The wrestlers, or “bökh” contestants, wear special costumes and perform a series of traditional pre-match ceremonies to honor the spirits and display respect for their opponents.
Archery
Archery has been an integral part of Mongolian culture for centuries. The traditional Mongolian bow, a composite recurve design, is a testament to the craftsmanship and skill of the ancient Mongolian archers. Archery competitions are often held during Naadam, the country’s largest and most significant festival, where participants showcase their prowess with the bow and arrow.

Horse Racing
Horse racing is deeply ingrained in the nomadic lifestyle of Mongolia. The country is renowned for its long-distance horse races, where young jockeys competitively ride across open steppes, showcasing
not only their riding skills but also their bond with the magnificent Mongolian horses. The annual Naadam Festival features some of the most prestigious horse racing events in the country.
Anklebone Shooting
Anklebone shooting, also known as “Shagain harhag,” is a traditional Mongolian game that involves skillfully flicking sheep anklebones at a target. This ancient game requires precision and accuracy, and it is often played as a form of entertainment during festivals and gatherings, showcasing the dexterity and coordination skills of the participants.
Famous Mongolian Celebrities and Personalities
Genghis Khan
Founder of the Mongol Empire, known for his military leadership and organizational skills.

Ankhmaa Gankhuyag
known professionally as Ankhmaa is a Mongolian singer, actress, and producer (born 1986 in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia).

Naidangiin Tüvshinbayar
He was the first Mongolian ever to win a gold medal at the Olympics.

Mongolia has produced a number of famous personalities who have made significant contributions to the arts, sports, and history. Genghis Khan, also known as Chinggis Khan, stands as one of the most prominent figures in world history as the founder of the vast Mongol Empire. His strategic prowess and leadership skills have left a lasting impact on the world. Similarly, Tserendorj Chuluunbat has won the hearts of many with his stellar performances in Mongolian cinema, portraying diverse characters on the screen. In the realm of music, Sarantsetseg Ganbaatar has mesmerized audiences with her melodious voice and preservation of traditional Mongolian music. Munkhbayar Dorjsuren has brought honor to Mongolia through his incredible feats in wrestling, demonstrating strength and skill on the international stage. Ankhmaa Gankhuyag, another notable figure, has made significant contributions in [add details about Ankhmaa Gankhuyag’s achievements and contributions here].
Mongolian History and Heritage
Great Mongol Empire
Led by Genghis Khan in the 13th century
Mongolian Civilizations
Rich history of nomadic tribes and ancient settlements
Buddhist Influence
Impact of Buddhism on Mongolian culture and heritage
Cultural Preservation
Efforts to safeguard and promote traditional Mongolian heritage
Mongolia has a rich and diverse history, with the Great Mongol Empire being one of its most notable periods. Led by the legendary Genghis Khan in the 13th century, the empire had a profound impact on world history. The country’s history also encompasses various ancient civilizations, including nomadic tribes and settlements, contributing to its unique heritage. Buddhism has been a significant influence, shaping Mongolian culture and traditions over the centuries. Efforts to preserve and promote traditional Mongolian heritage play a crucial role in safeguarding the country’s history for future generations.
Mongolian Nomadic Lifestyle
Nomadic Heritage
A way of life rooted in centuries of tradition.
Mobility and Flexibility
Moving with the seasons to find fresh pastures for livestock.
Traditional Dwelling
Living in gers, portable round tents made of wood and felt.
Sustainable Practices
Preserving the land and resources through sustainable nomadic methods.
The Mongolian nomadic lifestyle is deeply ingrained in the country’s history and culture. Nomadic herding is the foundation of this lifestyle, with families moving with their livestock to ensure they have access to fresh pastures and water sources. This mobility allows for a sustainable use of natural resources and promotes a deep connection to the land. The traditional dwelling, known as a “ger,” is a portable and durable tent that provides warmth and comfort in the harsh Mongolian climate. This lifestyle embodies the principles of mobility, flexibility, and sustainable practices, making it a unique and integral part of Mongolian heritage.
Mongolian Ger (Yurt) and Traditional Housing
A traditional Mongolian ger, also known as a yurt, is a portable, round tent covered with skins or felt and used as a dwelling by the nomadic people of Mongolia. The ger has been an integral part of Mongolian nomadic lifestyle for centuries, perfectly suited to the country’s harsh climate and the mobility needs of the nomadic herders.
Each ger is constructed with a wooden frame, traditionally made from latticed wood and bent to form a circular shape, and the exterior is covered with layers of felt and fabric, providing excellent insulation against the cold winters and hot summers of Mongolia.
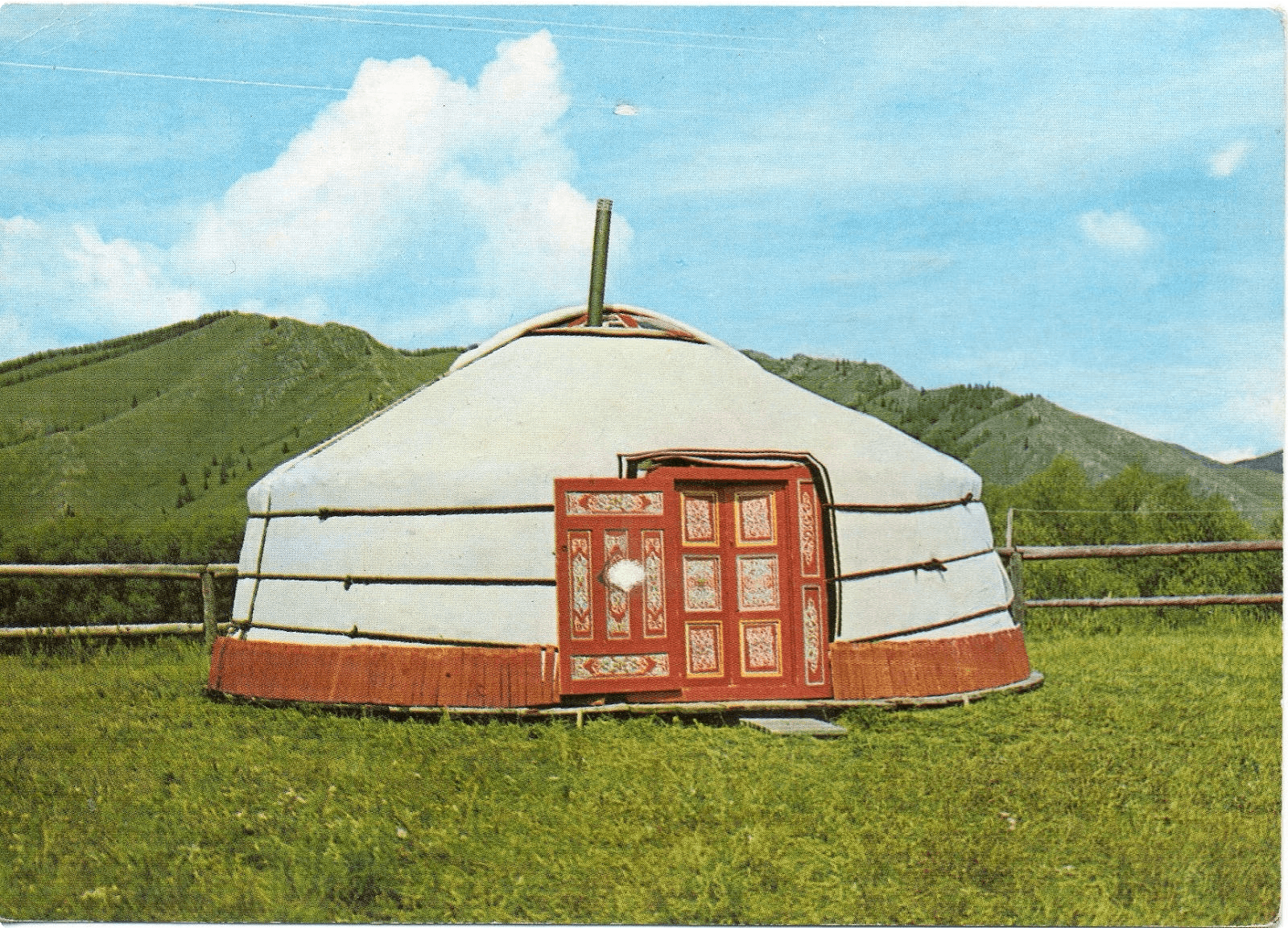
The interior of the ger is intricately decorated with vibrant colors, traditional patterns, and often features a central stove for heating and cooking. The layout and design of the ger reflect the deep connection between the Mongolian people and their natural surroundings, making it a fascinating symbol of their way of life.
Outside the ger, you will often find a wooden fence, known as a khana, used for keeping livestock and protecting the ger from strong winds. The nomadic lifestyle, centered around the ger, represents the enduring spirit and resilience of the Mongolian people.
For images, please search for “Mongolian ger interior” and “Mongolian nomadic lifestyle” to capture the essence of traditional Mongolian housing and the nomadic way of life.
Mongolian Language and Alphabet
Rich History: The Mongolian language has a rich history dating back to the Mongol Empire. It belongs to the Altaic language family and is written in the traditional Mongolian script which has its origins in the Uighur script.
Unique Script: The traditional Mongolian script is vertical and is written from top to bottom. It consists of 31 consonants and 6 vowels, and each character has a distinct shape and pronunciation.
Cultural Significance: The language and script hold great cultural significance, and efforts are made to preserve and promote them through education and cultural institutions.
Mongolian Religion and Beliefs
Buddhism
Buddhism has been a significant influence on the religious and spiritual beliefs of the Mongolian people. It is deeply rooted in the country’s history, and the majority of the population practices Tibetan Buddhism, often referred to as Lamaism. The monasteries, or “khiid,” hold an important place in Mongolian Buddhism, serving as centers of religious learning and meditation.
Shamanism
Shamanism is another vital aspect of Mongolian spirituality, deeply connected to the natural world and ancestral worship. Shamans, known as “buu,” play a crucial role in traditional ceremonies and rituals, acting as intermediaries between the human and spirit worlds. The reverence for nature and the belief in the spiritual power of natural elements are central tenets of shamanistic practices.
Symbolism and Folk Beliefs
Mongolian culture is rich with symbolism and folk beliefs, encompassing a wide array of traditions and customs. Symbols like the “Eternal Knot” and the “Three Jewels” hold immense significance, representing concepts such as eternity and enlightenment. Folk beliefs include reverence for the sky, mountains, and animals, with rituals and ceremonies honoring these elements.
Mongolian Art and Handicrafts
Thangka Paintings
Thangka paintings are a traditional form of Tibetan and Mongolian art. These intricate paintings often depict Buddhist deities, mandalas, and scenes from the life of Buddha. The process of creating thangka paintings is highly detailed, requiring specialized skills and techniques passed down through generations.

Felt Art and Crafts
Felt art and crafts are an integral part of Mongolian culture. Nomadic herders and artisans create intricate felt designs and crafts using techniques such as wet felting and needle felting. These crafts include items like traditional hats, garments, and decorative items with vibrant colors and unique patterns.
Wood Carving and Sculpture
Mongolian wood carving and sculpture exhibit exquisite craftsmanship and attention to detail. Artisans often carve wooden pieces with intricate patterns and designs, creating decorative objects, religious artifacts, and functional tools. The tradition of wood carving in Mongolia reflects the country’s rich cultural heritage and skilled craftsmanship.
Famous Landmarks and Monuments in Mongolia
Genghis Khan Statue Complex
The Genghis Khan Statue Complex is a monumental statue of Genghis Khan on horseback, located on the bank of the Tuul River in Tsonjin Boldog, near Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. The statue, which stands at 40
meters (131 ft) tall, is the tallest equestrian statue in the world. Visitors can take an elevator to the horse’s head to get panoramic views of the surrounding countryside.

Erdene Zuu Monastery
Erdene Zuu Monastery, located in Kharkhorin, is one of the oldest and most significant monasteries in Mongolia. Built in the 16th century, it was the first Buddhist monastery in Mongolia. The monastery complex encompasses an area of 400 square meters and is surrounded by a wall featuring 108 stupas. It is an important center of Mongolian Buddhism and a UNESCO World Heritage site.

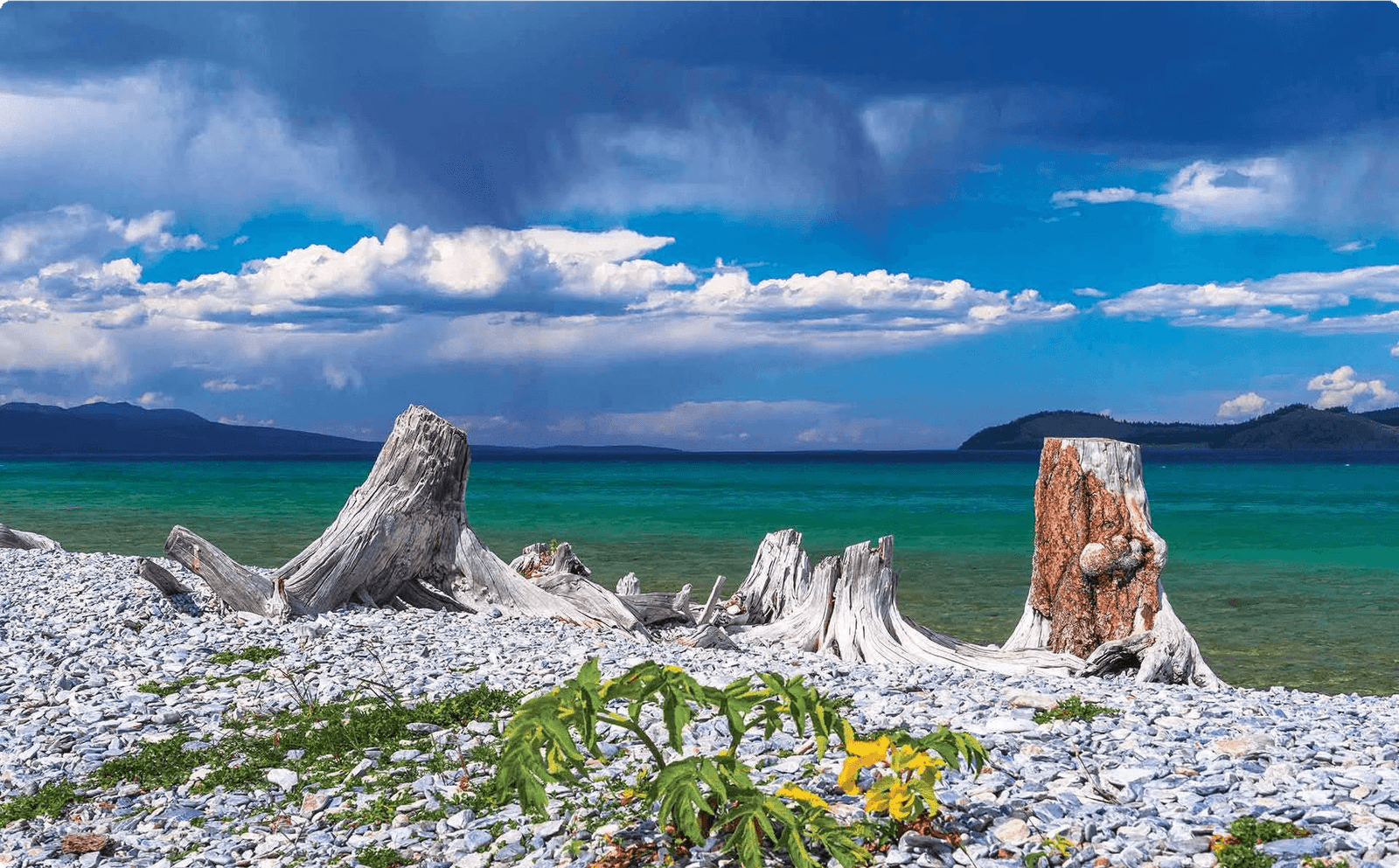
Khövsgöl Lake
Khövsgöl Lake, often referred to as the “Blue Pearl of Mongolia,” is a stunningly beautiful and pristine alpine lake located in the northwest of Mongolia. It is one of the 17 ancient lakes in the world, and it holds 70% of Mongolia’s freshwater. The surrounding Khövsgöl Lake National Park is a haven for outdoor enthusiasts, offering opportunities for hiking, horseback riding, and cultural experiences with the Tsaatan people.

Best Cities to Visit in Mongolia
Mongolia is a diverse and culturally rich country, offering a variety of unique and fascinating cities to explore. Each city has its own distinct charm, attractions, and culinary delights. Ulaanbaatar, the capital city, boasts the Tumen Ekh Song and Dance Ensemble, where visitors can experience traditional Mongolian music and dance performances. Additionally, the Gandantegchinlen Monastery is a must-visit for its grandeur and spiritual significance.
Erdenet, known for its proximity to the Orkhon Valley, offers a glimpse into Mongolia’s ancient history and is home to the Genghis Khan Square, a focal point for cultural events and gatherings. Darkhan, nestled amidst the Ar Khangai Mountains, provides breathtaking natural landscapes and opportunities for outdoor adventures. The local delicacies of Erdenet include aaruul (dried curds) and khorkhog (steamed mutton and vegetables).
Further east, Choibalsan invites visitors to explore the Fossil Cemetery and Galba Gorge, offering a unique perspective on Mongolia’s prehistoric past. The local cuisine in Choibalsan includes khorkhog (steamed mutton and vegetables) and bansh (steamed dumplings), providing a true taste of Eastern Mongolian flavors. Each of these cities offers a distinct experience, making Mongolia an enticing destination for travelers seeking cultural immersion and natural beauty.
Ulaanbaatar
Ulaanbaatar, the capital and largest city of Mongolia, is a vibrant and rapidly developing urban center nestled amidst the country’s vast steppes and rolling hills. With a unique blend of modernity and tradition, Ulaanbaatar offers visitors an enriching experience rooted in Mongolian history and culture.
The city is known for its bustling markets, where nomadic herders from the countryside trade their livestock and handmade crafts. The Gandantegchinlen Monastery, a prominent Buddhist site, stands in stark contrast to the city’s modern skyline, providing a peaceful sanctuary for both locals and tourists.

Ulaanbaatar’s rich cultural landscape is complemented by its thriving culinary scene, offering mouthwatering traditional Mongolian dishes alongside international cuisine. The National Museum of Mongolia and the Choijin Lama Temple Museum present fascinating insights into the nation’s history and heritage.
From exploring the imposing Sukhbaatar Square to discovering the treasures of the Bogd Khan Palace, Ulaanbaatar beckons travelers to immerse themselves in the allure of Mongolia’s past and present.
Erdenet
Cultural Diversity
Erdenet is celebrated for its ethnic diversity, with a large population of Russian, Kazakh, and other ethnic groups alongside Mongolians. This multicultural blend has enriched the city’s cultural tapestry, evident in its traditions, cuisine, and celebrations.

Copper Mining
Erdenet is known for its vast copper mining operations, which play a significant role in the city’s economy. The Erdenet Mining Corporation, one of the largest employers in the country, operates a massive open-pit copper mine, producing substantial quantities of copper concentrate for export.
Industrial Hub
With its focus on mining and heavy industry, Erdenet has evolved into a major industrial hub in Mongolia. The city boasts a range of manufacturing facilities and industrial infrastructure, contributing to the national economy and providing employment opportunities.
Darkhan
Rich Historical Heritage
Darkhan boasts a rich historical heritage, with its historical museum serving as a treasure trove of artifacts and exhibits showcasing the city’s past. From ancient artifacts to displays highlighting
significant events in Darkhan’s history, the museum provides visitors with a deeper understanding of the
city’s cultural and historical significance, making it an essential stop for history enthusiasts and those seeking to delve into Mongolia’s past.

Modern Urban Landscape
Darkhan, located in northern Mongolia, is a city known for its modern urban landscape. With tall buildings, bustling streets, and a vibrant city center, Darkhan offers a unique blend of tradition and modernity. The cityscape showcases the dynamic development and growth within the region, making it an intriguing destination for travelers seeking an authentic urban experience in Mongolia.
Vibrant Traditional Markets
Exploring Darkhan’s traditional markets is an immersive cultural experience. From colorful stalls offering local produce and traditional crafts to the lively atmosphere filled with the aromas of Mongolian cuisine, the traditional markets of Darkhan provide a glimpse into the daily life and cultural heritage of the community, making it a must-visit destination for those interested in traditional Mongolian lifestyle and commerce.
Choibalsan
Choibalsan City: Choibalsan is the fourth largest city in Mongolia, located in the eastern part of the country. It is the capital of Dornod Province, known for its rich history and cultural heritage.

Cultural Attractions: The city is home to fascinating cultural sites such as the Choibalsan Museum, where visitors can explore the history and traditions of the region. Additionally, the Choibalsan Theatre offers a glimpse into the performing arts scene of the city.
Nature and Wildlife: Surrounding Choibalsan, the beautiful landscapes and natural reserves provide opportunities for outdoor adventures and wildlife observation. The Khar Zurkhnii Khukh Nuur Lake and Guran Saikhan Mountain are popular destinations for nature enthusiasts.
Top Tourist Attractions in Mongolia
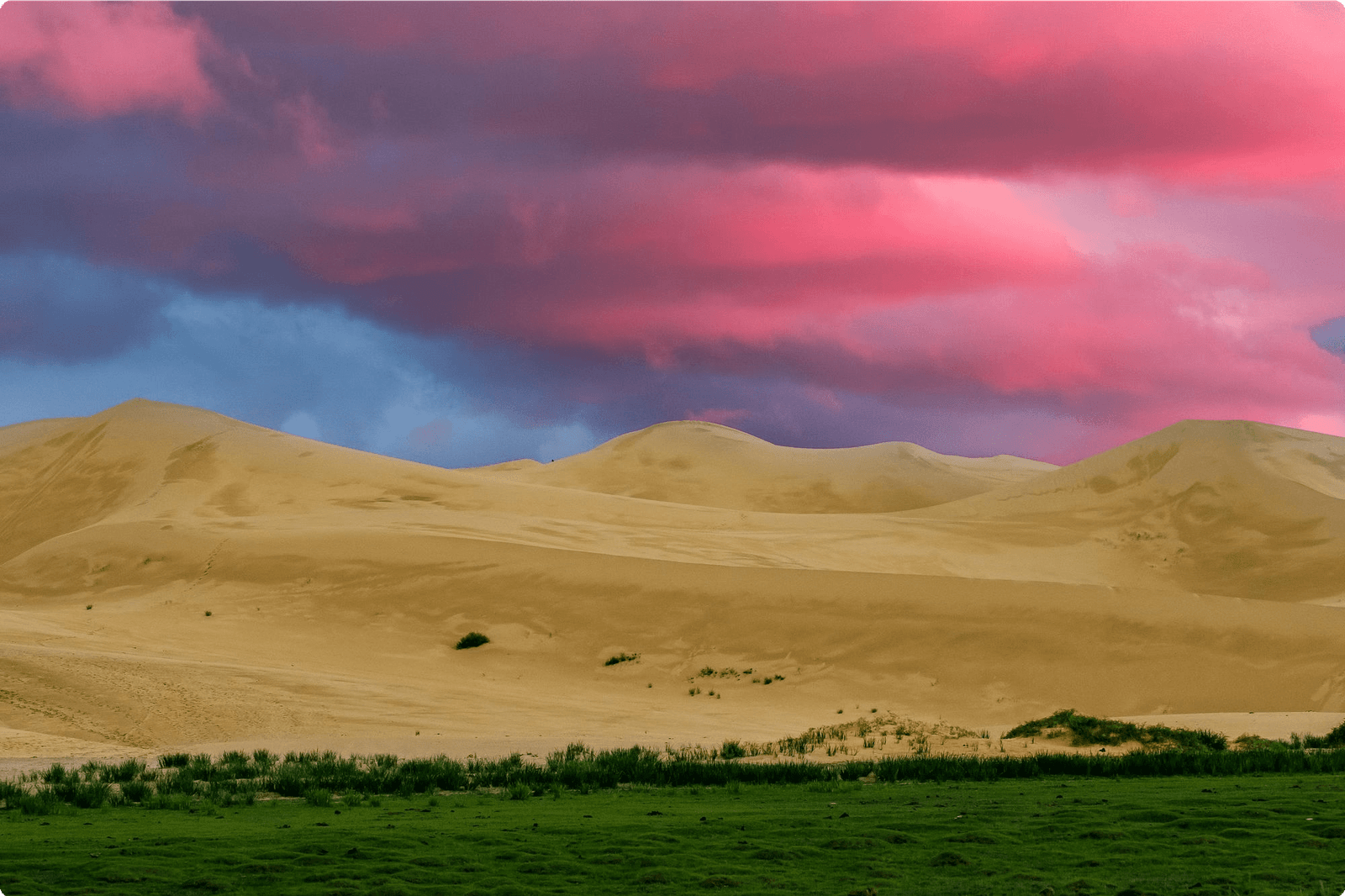
Gobi Desert
The vast desert landscape offers unique experiences such as camel treks, dune surfing, and exploring the Flaming Cliffs.

Lake Khövsgöl
Known as the “Blue Pearl of Mongolia,” this pristine lake is surrounded by lush forests and offers a range of outdoor activities.

Terelj National Park
This picturesque park is famous for its stunning rock formations, including the iconic Turtle Rock, and offers opportunities for hiking and horseback riding.

Erdene Zuu Monastery
As the oldest surviving monastery in Mongolia, it showcases beautiful architecture and holds significant historical and cultural value.

Natural Wonders and National Parks in Mongolia
Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert, one of the most remarkable natural wonders of Mongolia, spans across southern Mongolia and northern China. It features stunning sand dunes, rocky mountains, and unique flora and fauna, including the elusive snow leopard and the two-humped Bactrian camel.
Khuvsgul Lake
Khuvsgul Lake, often referred to as the “Blue Pearl of Mongolia,” is one of the world’s largest freshwater lakes, located in the northern part of the country. It’s surrounded by lush green forests and snow- capped mountains, offering breathtaking scenery and a tranquil environment for nature enthusiasts.

Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains, located in western Mongolia, are a true paradise for adventurers and outdoor enthusiasts. The pristine alpine lakes, rugged peaks, and diverse wildlife make it an ideal destination for trekking, mountaineering, and birdwatching.

Click here for more pictures
Terelj National Park
Terelj National Park, just a short drive from Ulaanbaatar, is known for its unique rock formations, picturesque valleys, and the iconic Turtle Rock. It provides an oasis of natural beauty and is a popular destination for camping, hiking, and horseback riding.
Adventure Activities in Mongolia
Horseback Riding
One of the most popular adventure activities in Mongolia is horseback riding. With vast open spaces and breathtaking landscapes, Mongolia offers the perfect setting for riding through the steppes on horseback. Travelers can join guided tours that allow them to experience the nomadic lifestyle and explore the remote countryside on horseback.
Hiking and Trekking
Mongolia’s diverse terrain, which includes mountains, deserts, and grasslands, provides ample
opportunities for hiking and trekking. From the stunning Altai Mountains to the Gobi Desert, adventurers can embark on challenging treks and hikes that offer stunning natural scenery and encounters with local wildlife.
Camel Trekking in the Gobi Desert
Exploring the vast expanse of the Gobi Desert on camelback is a unique and unforgettable adventure. Travelers can traverse the desert on a multi-day trek, experiencing the peacefulness of the desert, visiting oases, and camping under the star-filled sky, immersing themselves in the ancient tradition of camel travel.
Traditional Mongolian Medicine and Healing Practices
Healers and Shamans
In traditional Mongolian medicine, healers and shamans play a vital role in diagnosing and treating ailments. They use a combination of rituals, herbal remedies, and spiritual practices to heal physical and mental illness. The healers are highly respected in the community and often pass down their knowledge from one generation to the next.
Herbal Remedies
Mongolian traditional medicine relies heavily on the use of herbal remedies. The healers and practitioners have in-depth knowledge of local plants and their medicinal properties. These herbal remedies are often brewed into teas or ointments to address a wide range of health issues, from digestive problems to respiratory ailments.
Acupuncture and Bone Setting
Acupuncture and bone setting are common practices in traditional Mongolian medicine. Skilled practitioners use fine needles and hand manipulation techniques to balance the body’s energy and relieve pain. Bone setting, on the other hand, involves realigning misaligned bones and joints through manual adjustments, a skill passed down through generations.
Wildlife and Biodiversity in Mongolia
Mammals
Mongolia is home to a diverse range of mammal species, including the iconic Bactrian camel, snow leopard, Gobi bear, wild horse, and Siberian ibex. The country’s vast landscapes provide habitats for these and many other mammals, making it a haven for wildlife enthusiasts and conservationists alike.
Birds
The avian diversity in Mongolia is astounding, with over 450 species of birds recorded within its borders. From the majestic golden eagle used in traditional falconry to the elusive Altai snowcock, birdwatchers flock to Mongolia to witness its unique avifauna.
Reptiles and Amphibians
Mongolia is also home to various reptile and amphibian species, including the Siberian salamander, Mongolian toad, and several snake and lizard species. The country’s arid regions provide a suitable environment for these fascinating creatures.
Fish
Although Mongolia is landlocked, it boasts several freshwater fish species, with the Siberian sturgeon and Amur trout being among the notable inhabitants of its rivers and lakes.
Invertebrates
The invertebrate diversity in Mongolia includes a wide array of butterfly, beetle, and insect species, each playing a crucial role in the country’s ecosystems and biodiversity.
Sustainable Tourism in Mongolia
Preservation of Nomadic Lifestyle
Sustainable tourism in Mongolia focuses on preserving the nomadic lifestyle of the local herders. This includes promoting responsible and respectful interactions with nomadic communities, supporting traditional livelihoods, and raising awareness about the importance of nomadic culture and traditions.
Conservation of Natural Landscapes
Efforts are made to protect the pristine natural landscapes of Mongolia, including the vast steppes, remote deserts, and rugged mountains. Sustainable tourism practices prioritize conservation and sustainable use of natural resources, minimizing the impact on the environment while providing meaningful experiences for visitors.
Cultural Immersion and Authentic Experiences
Sustainable tourism in Mongolia aims to offer travelers the opportunity to engage in authentic cultural experiences. This may involve staying in traditional ger camps, participating in local festivals, learning about traditional crafts, and sharing meals with local families, providing an immersive and genuine glimpse into Mongolian life and culture.
Supporting Local Communities
Sustainable tourism initiatives place a strong emphasis on benefiting local communities. This includes creating economic opportunities for local artisans, guides, and small business owners, as well as contributing to the development of community-based tourism initiatives that empower local people and promote inclusive growth.
Conclusion and Summary of Mongolia
Mongolia is a land of rich cultural heritage, breathtaking natural landscapes, and a deep-rooted nomadic lifestyle. From its traditional music and dance to the sumptuous flavors of its food, Mongolia offers a truly unique experience for travelers. The country’s nomadic traditions, symbolized by the iconic Ger (Yurt) and the vast steppes, are an integral part of its identity. Additionally, the blend of Buddhism and shamanism in its religious beliefs adds a spiritual dimension to the Mongolian way of life.
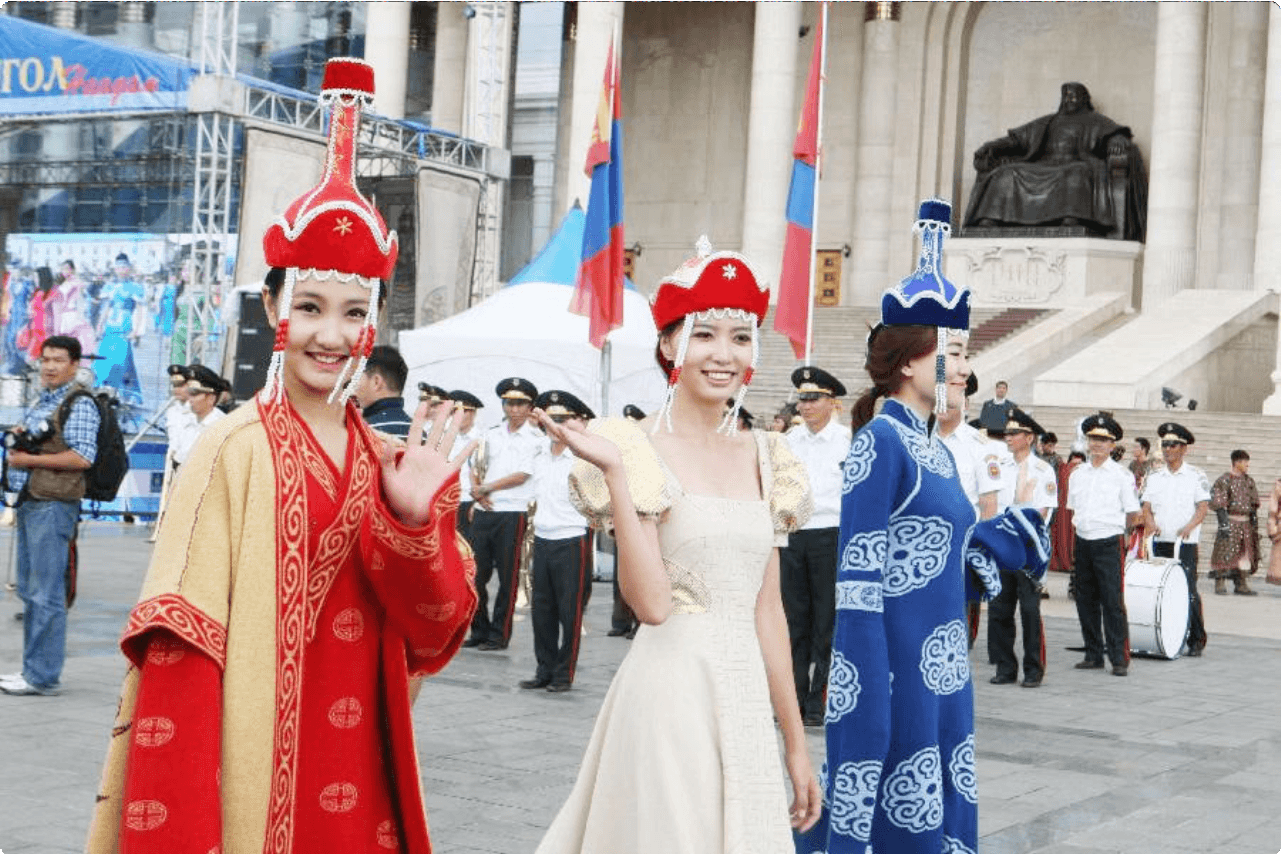

Exploring Mongolia means diving into a world where ancient traditions seamlessly coexist with modern influences. The warmth of its people, the rugged beauty of the Gobi desert, and the nomadic horse culture all combine to create an unforgettable adventure. As you journey through the expansive landscapes and vibrant cities, you’ll discover a land that is as diverse as it is captivating.
This brief overview only scratches the surface of what Mongolia has to offer. Whether it’s the history, the art, or the natural wonders, there’s always something more to explore and experience in this remarkable country.
One Comment
tlover tonet
You have brought up a very wonderful points, thanks for the post.